Week 05: Electronic Production
Group assignment
Characterize the design rules for your PCB production process
Design rules
In Fablab-CIT, we have the Roland MDX-540 CNC milling machine, which we use for the manufacture of electronic boards and 3D machining in some materials, such as machinable wax, plaster, etc.

For the tests, we decided to use a 1/64" conical endmill at an angle of 45°

The following example is used to perform the machining, it should be noted that the resolution of the PNG image on which the CAM will be made must be 1024 px.

To make the CAM, we use the resource offered by the Fab Academy network, that is fabmodules. On the page we select the PNG image on which we will work, the output format must be .nc corresponding to the G code, and in PCB traces we place the option of our 1/64". We adapt the parameters to the recommended ones, 8000 RPM, tool diameter of 0.1 mm and number of offsets of 15.

Once the code g is obtained, we proceed to turn on the router, place the plate on which it will work, calibrate the machine following the same steps that can be seen in the personal repositories of each CIT member and load the code to the milling machine. For these tests we decided to use boards of different materials, first ceramic and then fiberglass to compare the differences in quality.
Ceramic

Fiberglass
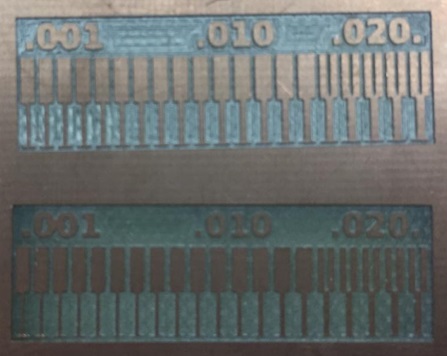
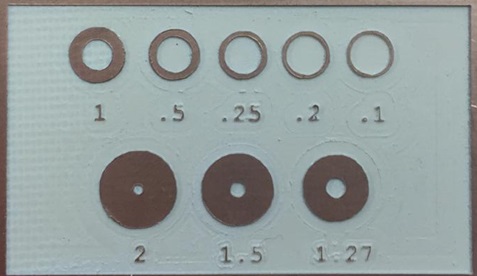
As we can see, the ceramic board has a better finish even though the same endmilling was used for both diameters. We also did tests of figures with curvatures, and this was the result.
Additionally, we test with an alternative method, manufacture of electronic board using ferric acid. The first step is to print the desired image on coated paper using a laser printer.

Then a thermal plate at 190 degrees Celsius is used to adhere the image to the electronic board. The copper-containing side must be sanded first. Subsequently, it is immersed in acid for approximately 15 minutes, the acid will corrode the areas with copper, except for the black areas.

This test was carried out in both ceramic and fiberglass.

As you can see, there are blackened areas, so it must be sanded. The following result is in the next picture.
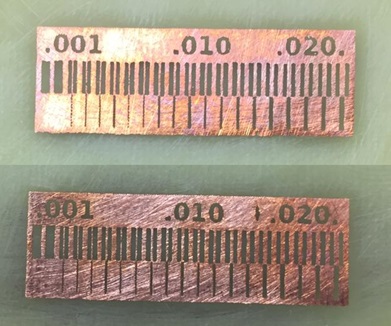
Finally, as can be seen, the acid eliminated the white areas of the original picture, for this reason the colors had to be inverted before printing on coated paper. Although this method allows to manufacture electronic boards in greater quantity and less time, it does not have a good finish in small designs, since it depends on the quality of the printing. It is concluded that the optimal process is milling using Roland MDX, using ceramic material plate.